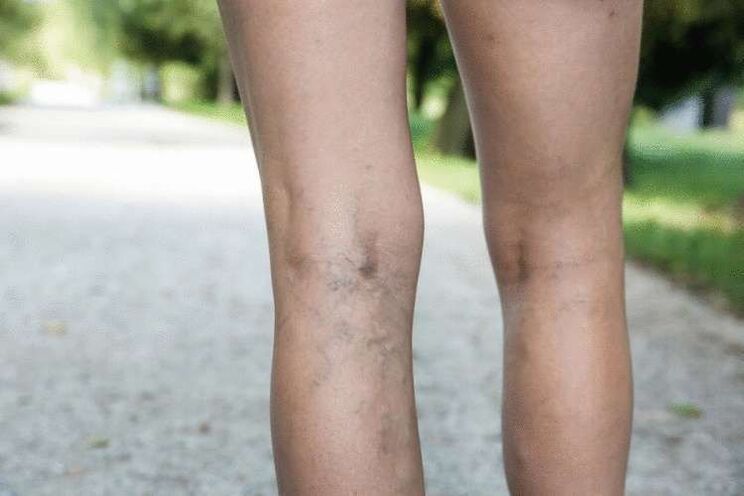
Varicose veins are divided into subspecies, each of which has its own characteristics. Treatment depends on the degree of the disease, the causes that caused it, concomitant pathologies and other factors.
Description of the disease
In short, everything about varicose veins is a disease in which the outflow of blood is disturbed, its stagnation appears. This leads to bloating of the veins and their serpentine tortuosity. The disease is quite common, occurring in about a quarter of the population.
In adolescence, venous expansion develops with equal frequency in both sexes. In adulthood, women are twice as likely to be at risk. Vein problems are caused by severe hormonal changes that occur during the menstrual cycle or during pregnancy.
As a result, the tone of the vessels weakens greatly, they begin to expand, and the venous blood supply is disrupted. A diagnosis of vbvnc is made (otherwise - varicose veins of the lower extremities).
Development mechanism
The veins of the legs form a network with many ramifications, which are connected by perforators. Through the superficial blood veins, an outflow from the epidermis and its tissue takes place, through deep ones - from other tissues. Perforating vessels equalize venous pressure. In a normal state, the blood flow moves only towards the deep ones. From the periphery to the middle - due to the remaining blood pressure and tendon pressure.
When this process is disrupted, peripheral veins swell, become blue and twisted. At the same time, varicose nodes appear, the valve circuit is destroyed, and vein dilatation appears. The outflow of blood cannot follow the usual pattern. This is accompanied by reflux of the veins. Spider veins appear. Closed valves in the veins do not let the blood go up. Stagnation of blood is formed, pressure rises in the arteries.
As soon as it gets very high, blood begins to be pushed out. Its excess amount stretches the venous walls and blood vessels, forming intradermal varicose veins. The edges of the capillaries strongly lean against the dermis and shine through it, forming vascular networks. Such places are very weak, their color is becoming more noticeable. Nodules on the legs become clearly visible (what varicose veins look like is shown in the photo). High blood pressure contributes to atrophy of muscle fibers, nerves involved in venous tone die.
Classification of the disease
The disease can manifest itself in different areas. More common are varicose veins on the hips and legs. The disease has several classifications. This is due to many variants of the course and sites of damage.
Stages of varicose veins:
- Compensation A. The patient does not complain about anything, but the visual examination reveals the presence of swollen veins in the legs. These are the first signs of the disease.
- Subcompensation B. The blood veins on the legs are greatly expanded. Patients complain of distention in the limbs, night cramps. In the evenings, there is slight swelling of the veins in the feet, legs and ankles. These symptoms disappear in the morning.
- With decompensation, eczema, dermatitis and itching in the epidermis are added to the above symptoms. The skin begins to shine, becomes dry and dense. Small hemorrhages are visible under the surface.
This classification reflects the levels of venous insufficiency, the form of vein swelling and some complications.
Classification by shape
The disease is divided into several types:
- segmental varicose veins;
- main (with two subspecies - in the small or large saphenous vein);
- perforating;
- reticular.
International classification
According to the international classification, varicose veins of the lower extremities are divided into six classes, due to certain characteristics:
- zero - there are no other symptoms of the disease, except for heaviness in the legs;
- the first - the venous mesh and asterisks are visually visible, at night a person is twisted by cramps in the muscles;
- the second - some veins begin to expand;
- the third - there is swelling of the legs, which does not go away even after a short rest;
- fourth - there is hyperpigmentation of the legs, dermatitis;
- fifth - ulcers are formed;
The sixth class of varicose veins on the legs is diagnosed when skin lesions have developed into trophic and become persistent.
Causes of occurrence
The causes of varicose veins are very diverse - from improper lifestyle and diet to congenital pathologies. Varicose veins occur due to a violation of the circulatory system.
Its causes of occurrence:
- Hereditary predisposition. Children whose parents had varicose veins can get this disease in 70 percent of cases. At the same time, signs of varicose veins often appear at an early age.
- Disruption of the endocrine and hormonal systems. The risk group is mainly women, due to the anatomy of the body. Ladies have an insufficient amount of estrogen, and corpus luteum hormones predominate. They have a relaxing effect on the muscles, reduce the elasticity of the vein walls. The most dangerous varicose veins on the legs in women during childbearing, breastfeeding, menopause. The risk zone for both sexes is the ripening period.
- Stress, depression, nervous disorders reduce the tone of the veins. Their elasticity is regulated by nerve endings.
- Pelvic inflammation damages the small blood veins.
- Why does varicose veins appear with insufficient mobility, office work? When a person is sitting, his veins are strongly pinched. As a result, blood circulation is impaired and the tone of the channel walls decreases. Liquid begins to stagnate in it, which leads to the expansion of the veins.
- Increased physical activity, which includes lifting weights, prolonged leg work, obesity, pregnancy. Against the background of the above, the pressure in the veins increases greatly.
- Various neoplasms, blood clots that impede the outflow of blood.
- Flat feet.
- Diseases and injuries.
- Constipation, in which pressure builds up in the abdomen.
- Arterial-venous "crossroads" where arterial blood cell overflow can occur.
- Too high heels. The risk of varicose veins increases significantly if you move around on them for a long time.
- Chronic liver diseases - cirrhosis, all types of hepatitis, etc.
- Body structure. People who are above average height are more likely to suffer from varicose veins.
Another cause of varicose veins of the lower extremities is upright posture. A great load falls on a person's legs. The blood column extends from the lower extremities to the heart muscle, so those who spend a lot of time in a standing position are at greatest risk.
Symptoms of varicose veins
The symptoms of varicose veins begin with heaviness in the legs. Many people confuse this feeling with banal fatigue.
The disease begins to progress, and new symptoms appear:
- there is a thickening of the vein;
- pain in the legs;
- evening swelling of the legs;
- veins throb;
- burning under the skin;
- nocturnal muscle cramps;
- redness of the affected areas;
- veins begin to expand;
- the skin of the lower leg becomes dark, with seals;
- numbness of the legs.
Sometimes the symptoms of varicose veins appear only in the popliteal region or behind the legs. These signs are less noticeable if the limbs have excessive hairiness or thick skin.
Varicose veins on the legs are easily determined by palpation. In this case, the tortuosity of the veins is felt. If the patient's legs are raised, then the venous mesh disappears, in an upright position it thickens.
Dull lobes, burning sensation, and cramps often appear after standing for a long time. Feet swells mainly in the soft tissue area - in the lower part of the lower leg, in the ankles. If varicose veins are not treated, then the deformation affects and affects the skin. It acquires a bluish tint, swells quickly. Additional symptoms appear:
- induration;
- severe muscle pain that becomes more intense when walking
- varicose ulcer;
- pigmentation;
- veins respond with soreness when palpating;
- insufficient nutrition of the epidermis.
When varicose veins of the lower extremities go into a complicated stage, additional weakness and fever appear. More rarely, bleeding occurs due to a ruptured vein. This phenomenon appears most often at night.
Diagnostics
Only a vascular surgeon or phlebologist can accurately determine varicose veins. Doctors should be consulted at the first sign of the disease. First, a visual examination of the patient is carried out, palpation of the allegedly damaged areas. To clarify the diagnosis, additional diagnostics of varicose veins is carried out:
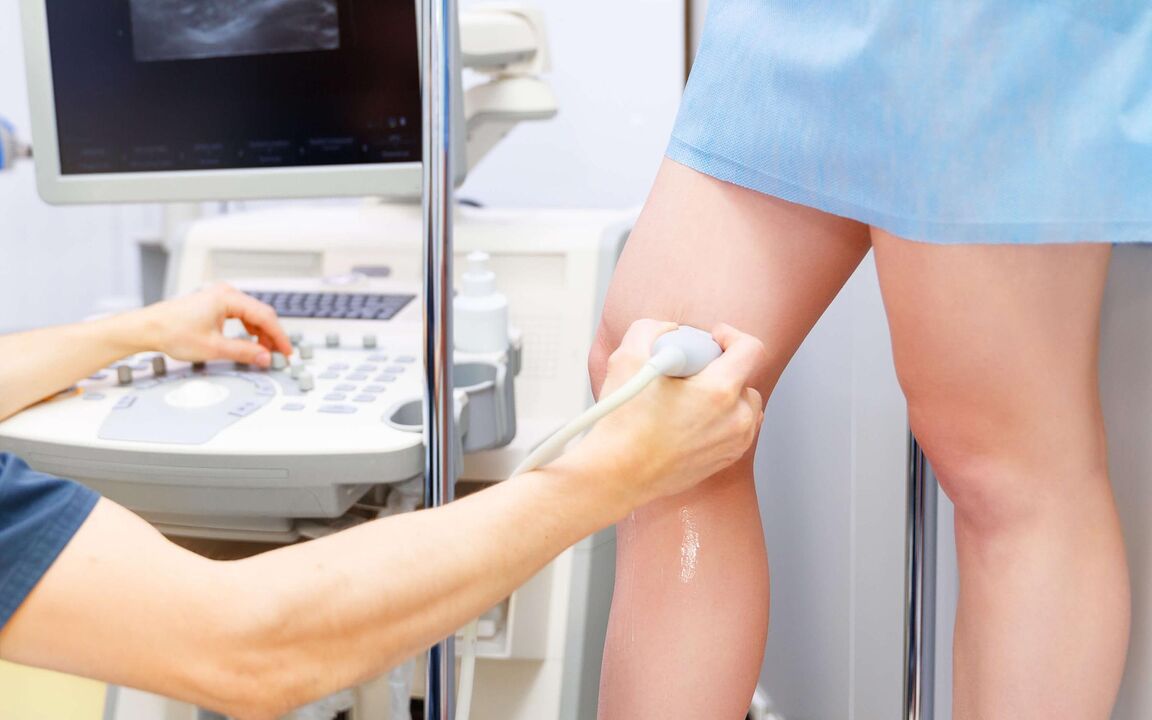
- Ultrasound examination, during which not only pathology is determined, but also the directions of blood flow, the presence of neoplasms and blood clots are seen. The procedure allows you to assess the degree of vascular dilatation.
- Contrast venography is the most informative and accurate method. It allows you to assess the venous state as accurately as possible. To do this, before the procedure, a contrast agent is injected into the patient's body, which stains the blood.
The methods are interchangeable. However, ultrasound is less invasive, so this method is preferred. Determination of the severity of deformities and disorders is carried out using X-ray and rheovasography.
Treatment of the disease
For the treatment of varicose veins, a complex treatment is initially prescribed. It includes several directions. The main thing is drug treatment. At the initial stage, venotonics are prescribed in the form of ointments and gels. They protect the vascular walls, accelerate outflow and improve blood circulation.
Preparations for diseases of the veins are used in courses, reduce pain and swelling. However, ointments and gels do not have a strong effect; they are used in the early stages of the disease. Venotonics are also available in tablets. They are prescribed to eliminate deep varicose veins:
- Saponite.
- Diosmin based.
- Rutosides eliminate inflammation.
Phlebectomy of the lower extremities is performed using injections or elastic bandaging. The puncture method is used before, during and after operations. Catheter view - only during the period of surgery. Isolated sclerotherapy does not give stable results, and will not stop the exacerbation of the disease. More often it is combined with surgical treatment. Phlebosclerosis therapy has contraindications:
- obliterating endarteritis;
- acute thrombophlebitis of the extremities;
- diabetic angiopathy;
- blood clotting disorders;
- pregnancy;
- atherosclerosis with ischemic disease;
- allergic reactions to the constituents of the drugs.
Additionally, drugs are prescribed that improve blood circulation - low molecular weight dextrans. They reduce the viscosity of the blood, increase the elasticity of blood vessels and participate in the breakdown of platelets. This improves microcirculation and tissue oxidation.
Also, for diseases of the veins, anticoagulant drugs of direct and indirect action are prescribed. They reduce the risk of blood clots.
At the same time, external decongestants are used. They reduce inflammation and prevent blood clots. Non-steroidal tablets for varicose veins relieve pain and inflammation, prevent their spread.
Physiotherapy
Treatment of varicose veins in the legs is possible with a puncture method. It can be classified as physiotherapy, as it is often performed in the surgeon's office. First, large veins are blocked, then smaller ones. Before the introduction of the drug, the patient lies on the couch. For a long vessel or several located around the circumference of the leg, more than one therapy session is done.
Physiotherapy for varicose veins includes a new direction of treatment - vein obliteration with radio frequency radiation. This method does not cause more trauma to the vessels, has a slight soreness and prevents possible complications. The efficiency of the method is high. Radiation destroys the affected vessel walls, while healthy ones remain unaffected. Vein gaps disappear.
Pneumatic massage can be prescribed, which is carried out using a small device. During the session, tissue trophism and blood circulation improve. Some of the symptoms of varicose veins are significantly weakened.
Surgical operations
The decision to operate on the veins of the lower extremities is made by a vascular surgeon or phlebologist. They also give other recommendations for varicose veins. For example, for pregnant women, if the disease is not dangerous, it is proposed to postpone surgery until the baby is born.
During gestation, varicose veins of the legs in women progresses and the results achieved by the operation may disappear. Then re-intervention will be required. Surgical treatment can be performed in several ways:
- Combined phlebectomy is the most common method. It is used for severe varicose veins. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Minimal incisions are made through which a special probe with a phleboextractor is inserted. Then it is taken out and the vein is excised from the groin to the middle of the lower leg. Small blood veins and ducts are removed through the punctures. This operation is called miniflebectomy.
- Endovasal electrocoagulation is accompanied by the removal of veins using a current. The method is more dangerous than conventional surgery or obliteration.
- Cryotherapy is used to remove blood veins using low temperatures. The method is safe, but it can be difficult to determine the required depth of freezing so as not to damage the nearby tissues, therefore, the treatment of varicose veins in this way is used extremely rarely.
- Sclerobliteration of veins is done by inserting a catheter under the skin. Prior to this, the required veins and sections are marked. Then the anastomosis is exposed on the large blood vessel, and the tributaries are tied up. Perforating veins are pinched from the incisions. A catheter is inserted into the cut-off vein. Then the vein is sutured and the wound is bandaged. A gauze roller is laid along the entire vein and pressed against the leg. When the catheter is removed, a venosclerosant is injected.
- Endoscopic dissection of perforating veins allows the affected veins to be ligated, thereby excluding them from the general circulation. For this, special probes are used. Another similar method is transillumination phlebectomy.
Laser coagulation is done using special equipment. The affected blood vein is sealed from the inside with a laser beam. As a result, the vein is excluded from the general circulation.
Home treatment
Before treating varicose veins on the legs, you need to consult a doctor. He can prescribe systemic drugs, leech therapy. Latent internal varicose veins can be diagnosed. It is impossible to cure it at home. For mild disease, apple cider vinegar and cabbage leaf are commonly used.

To cure varicose veins, you need to wear compression underwear, do elastic bandaging. However, any treatment at home will be ineffective in the advanced stage of the disease. Leeches are an unconventional method of therapy. Home treatment with hirudotherapy can only be used under the supervision of a specialist. You cannot do the procedure yourself.
Complications of varicose veins
If varicose veins are not treated in time, the disease can cause serious complications. These include:
- dermatitis;
- eczema;
- acute thrombophlebitis of superficial blood veins;
- phlebothrombosis;
- hypoxia;
- bleeding in varicose veins;
- trophic ulcers.
With the progression of varicose veins on the legs, varicothrombophlebitis appears, and then lebothrombosis. It captures deep veins, pulmonary embolism begins. If varicose veins are not stopped at this stage, vascular occlusion develops, and after stopping the outflow of blood, gangrene. This is fraught with at least limb amputation.
Prophylaxis
Before treating varicose veins, you need to consult a doctor. Perhaps, there will be enough light venotonics and adherence to preventive measures so that the disease does not progress. It is necessary to reduce excessive physical activity, you can not stand for a long time - it is better to move, the sitting position is periodically replaced by a lying position. If this is not possible, at least make circular movements with your feet.
After a hard day, your tired legs need to be held in an elevated position. Try to avoid putting one foot on the other for a long time. It is necessary to maintain an optimal weight, with obesity - go on a diet. Avoid wearing things that compress your groin, legs and waist.
It is advisable to take daily walks in the fresh air, actively engage in swimming or cycling. It is recommended to do exercises every morning and evening. It is important to give up bad habits - smoking, alcohol consumption. It is useful to take a contrast shower.
It is possible to treat varicose veins in the early stages with ointments and gels, light medications. However, for a progressive disease, cardinal surgical methods are required, which are combined with compression and sclerotherapy.

















